|
1 |
Launch Excel. |
||
|
2 |
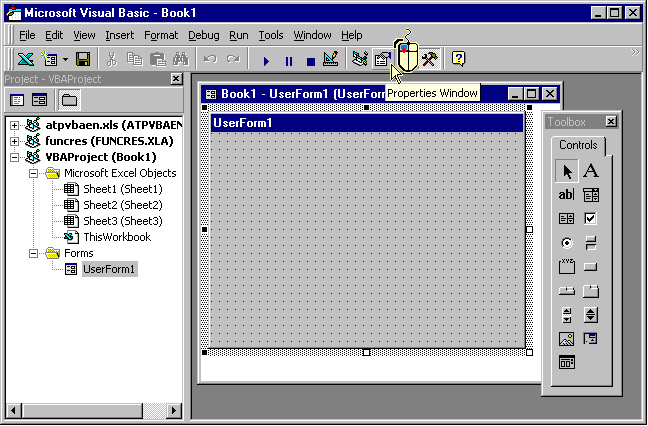
Use the Tools | Macro | Visual Basic Editor command. |
||
|
3 |
In the Project - VBAProject window, right-click the Microsoft Excel Objects folder. |
||
|
4 |
From the Shortcut menu, select options Insert and UserForm options. |
||
|
|
|||
|
5 |
If the Properties windows is not open, click the Properties Window button. |
||
|
6 |
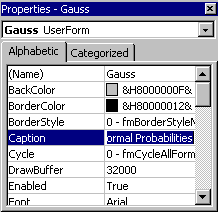
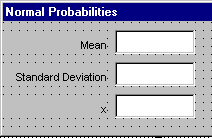
The form window shows the UserForm1 title. In order to change it to Normal Probabilities, click the form and then double-click its Caption property in the Properties window. Finally, enter text Normal Probabilities. Also change the Name property of the form to Gauss. |
|
|
|
7 |
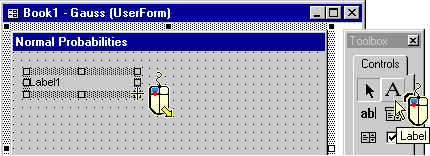
Click the Label control in the Toolbox window and draw a box for the label on the form. In the Properties window, change the label's Caption to Mean.
|
||
|
8 |
In a similar way, create two other labels: Standard Deviation and x. |
|
|
|
9 |
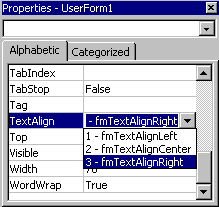
Using the Shift+Click method, select all the labels. Scroll through the properties to reveal the TextAlign property and chang it to 3-fmTextAlighRight. |
|
|
|
10 |
Click the TextBox control in the Toolbox window and draw a box for this control on the form. In the Properties window, change the control's Name to txtMean.
|
||
|
11 |
In a similar way, create two other TextBox controls: txtStandardDeviation and txtX. |
|
|
|
12 |
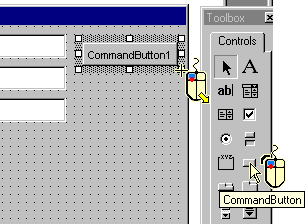
Click the CommandButton control in the Toolbox window and draw a box for this control on the form. In the Properties window, change the control's Name to cmdOK. Also change the Caption property of this control to OK. |
|
|
|
13 |
In a similar way, create the Cancel CommandButton control (Name = cmdCancel and Caption = Cancel). |
||
|
14 |
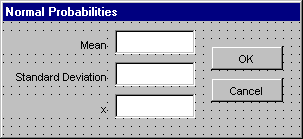
Finally, resize the form window so it will look like this one:
|
||
|
15 |
It is a good time to save your work. Save the entire workbook as XLDlgBox.xls. |
||
|
16 |
To add program code to this from, double-click the OK button. Excel VB takes you to the cmdOK_Click procedure, where you will write a few statements to calculate Normal probabilities P(X <= x) and P(X > x): |
||
|
Private Sub cmdOK_Click() |
|||
|
Mu = txtMean.Text |
|||
|
End Sub |
|||
|
Note: |
|||
|
txtMean.Text is a (value) property of the TextBox txtMean. |
|||
|
17 |
Close the Code window and double-click the Cancel command button. Excel VB opens the Code window again and starts up the cmdCancel_Click procedure. The only statement in this procedure is Unload Me. Then close the Code window. |
||
|
Private Sub cmdCancel_Click() |
|||
|
Unload Me |
|||
|
End Sub |
|||
|
18 |
In the Project - VBAProject window, right-click the Microsoft Excel Objects folder. From the Shortcut menu, select options Insert and Module options. |
||
|
19 |
Name the module as NormalProbability. |
||
|
20 |
In the module's Code window, define the following procedure: |
||
|
Sub GetNormalProbabilities() |
|||
|
Gauss.Show |
|||
|
End Sub |
|||
|
21 |
Via the Taskbar, go back to Excel worksheet and choose Tools | Macro | Macros | GetNormalProbabilities | Run. |
||
|
22 |
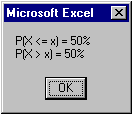
Enter 0 for Mean, 1 for Standard Deviation, 0 for x, and click OK. |
||
|
|
|||
|
23 |
Click the Cancel button. |
||